
Risk-Aware Bidding for VPPs with Power-to-Hydrogen
How hydrogen storage helps virtual power plants bid more strategically and manage market risk under renewable uncertainty.
🔋 Risk-Aware Bidding for VPPs with Power-to-Hydrogen
A clear and intuitive explanation of how hydrogen improves VPP bidding.
Figure 1. VPP can reduce congestion and redirect flows more efficiently.(Image source: Toshiba)
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) bring together distributed resources—such as solar, wind, batteries, and now hydrogen systems—to operate like a flexible power plant in electricity markets.
But there’s a challenge:
Electricity markets are volatile, and renewable output is uncertain.
A poor bidding strategy can lead to major financial losses.
This post explains how Power-to-Hydrogen (P2H) and risk-aware optimization help VPPs make smarter bidding decisions.
⚡ Why Bidding Is Hard for VPPs
VPP operators must decide how much energy to bid into the market ahead of time.
However:
- Solar and wind output fluctuate
- Prices move unpredictably
- Overbidding can cause penalties
- Underbidding loses opportunities
Most VPPs rely on batteries (ESS) to buffer uncertainty, but batteries alone are often not enough.
This is where hydrogen enters the picture.
🔋 Why Hydrogen Helps VPPs
A Power-to-Hydrogen system includes:
- Electrolyzer → converts electricity into hydrogen
- Hydrogen tank → stores hydrogen for long periods
- Fuel cell → converts hydrogen back to electricity
Compared to batteries, hydrogen offers:
- Much larger storage capacity
- Ability to charge and discharge simultaneously
- Better economic potential as hydrogen prices drop
- Flexibility for multi-energy markets (electricity + hydrogen)
Hydrogen essentially acts as a deep buffer that smooths uncertainty.
📉 The Risk Issue: Market Volatility
Even with hydrogen, the VPP faces financial risk:
- Low renewable output → must buy expensive electricity
- High renewable output → prices may drop unexpectedly
- Extreme scenarios (tail events) → major losses
To protect against these risks, we use CVaR (Conditional Value-at-Risk) — a common tool in finance for controlling downside risk.
🧠 The Proposed Approach: A Risk-Aware Bi-Level Model
In this regard, we introduces a bi-level optimization structure:
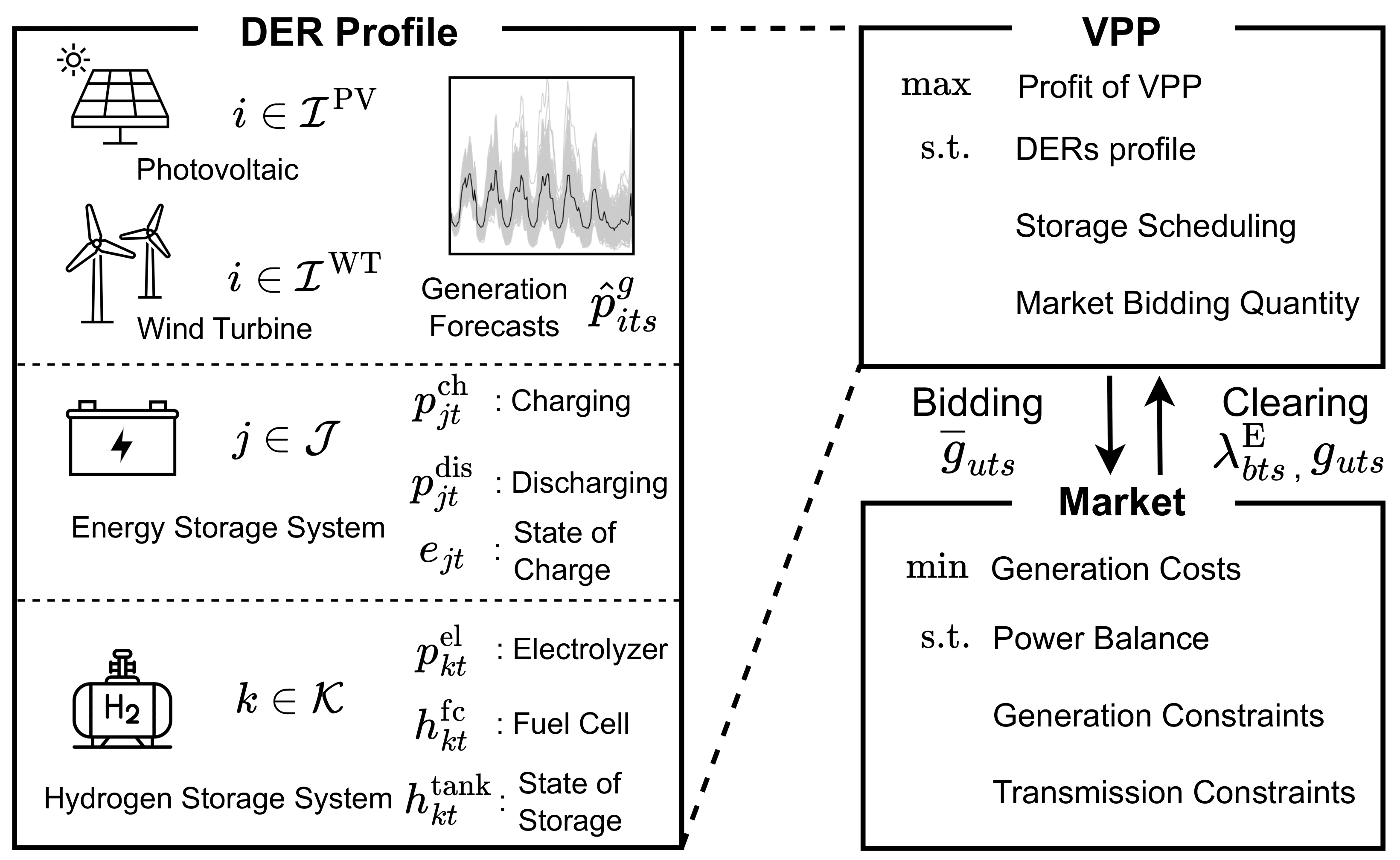
Figure 2. High-level representation of the bi-level bidding framework.
🔼 Upper Level — VPP’s Decision
The VPP chooses:
- How much energy to bid
- How to operate battery + hydrogen system
- How risk-averse to be (via CVaR parameter)
Goal:
Maximize profit while limiting downside financial risk.
🔽 Lower Level — Market Clearing
The electricity market:
- Clears demand and supply
- Determines Locational Marginal Prices (LMPs)
- Applies power flow and congestion constraints
This ensures the VPP’s bids are physically feasible.
The bi-level structure captures how market physics reacts to the VPP’s decisions.
🧩 Key Insights from the Study
1️⃣ Hydrogen Increases Profitability
| Portfolio | Revenue ($) |
|---|---|
| Solar + Wind | 3,710 |
| + Battery | 4,405 |
| + Hydrogen | 4,607 |
Hydrogen-enabled VPPs outperform battery-only systems because:
- They can shift energy across long time scales
- They can exploit price volatility better
- Fuel cells + electrolyzers provide unique flexibility
2️⃣ Bigger Hydrogen Tanks Reduce Risk
| Tank Size | Revenue Impact |
|---|---|
| 0.5× | −5.6% |
| 1× | baseline |
| 2× | +4.9% |
Larger tanks help the VPP remain profitable even under uncertain renewables and prices.
3️⃣ CVaR Controls Financial Exposure
By adjusting a single risk-aversion parameter (β), the VPP can:
- Reduce losses in bad scenarios
- Stabilize revenue
- Prevent aggressive bidding when renewable output is low
Higher β → more conservative bids → lower risk.
4️⃣ Hydrogen Performs Better Under Risk Than Batteries
Hydrogen-based VPPs are:
- More resilient to low-renewable scenarios
- Better at capturing high-price opportunities
- Less sensitive to market volatility
This makes hydrogen a future-proof energy storage option.
📘 Why This Matters
Risk-aware bidding with hydrogen enables:
✔ Higher profits
✔ Lower exposure to extreme losses
✔ More stable VPP operation under uncertainty
✔ Better use of renewable energy
✔ A path toward multi-energy market participation
As hydrogen infrastructure grows, VPPs will play a crucial role in linking electricity, hydrogen, and storage markets.
🔭 Future Extensions
The research suggests several directions:
- Real-time bidding
- Joint electricity–hydrogen scheduling
- Multi-day CVaR strategies
- Interaction with congestion forecasting
- Coordinated bidding among multiple VPPs
📘 Reference
Yoo, J., & Kim, J. “A Risk-aware Bi-level Bidding Strategy for Virtual Power Plant with Power-to-Hydrogen System.” 2025 IEEE PES General Meeting (PESGM). [link]